Russian War Report: DFRLab confirms aerial strikes on industrial plants north of Bakhmut
As Russian forces continue their offensive on Bakhmut, the DFRLab examined satellite imagery to reveal the potential of missile attacks.
Russian War Report: DFRLab confirms aerial strikes on industrial plants north of Bakhmut
Share this story
THE FOCUS

As Russia continues its assault on Ukraine, the Atlantic Council’s Digital Forensic Research Lab (DFRLab) is keeping a close eye on Russia’s movements across the military, cyber, and information domains. With more than seven years of experience monitoring the situation in Ukraine—as well as Russia’s use of propaganda and disinformation to undermine the United States, NATO, and the European Union—the DFRLab’s global team presents the latest installment of the Russian War Report.
Security
Tracking narratives
International response
DFRLab confirms aerial strikes on industrial plants north of Bakhmut
Russian armed forces continue their offensive inside the contested city of Bakhmut. At the time of writing, the western part of Bakhmut remained under Ukrainian control, with the Bakhmutka River acting as a buffer zone between the artillery and infantry forces deployed on either side of the waterway. Russian missile and aerial strikes targeted intermediary positions to push back Ukrainian armed forces, from Yahidne in the north towards Bakhmut industrial plants.
The DFRLab collected open-source satellite imagery dating back to the first two weeks of March to document missile strikes on an industrial plant in the north of Bakhmut. The imagery was collected from the European Space Agency’s Sentinel hub using images provided by satellite constellation Sentinel-2.
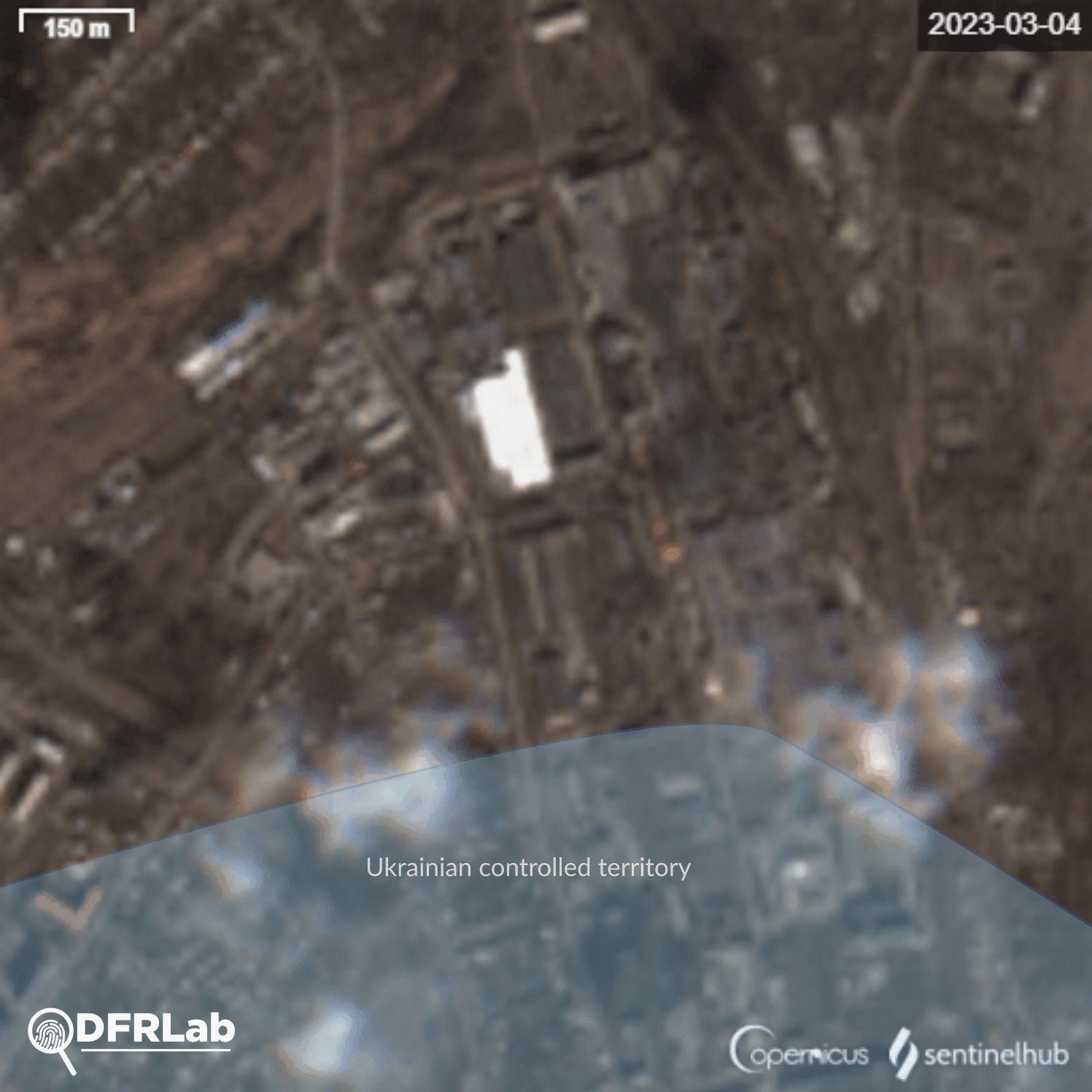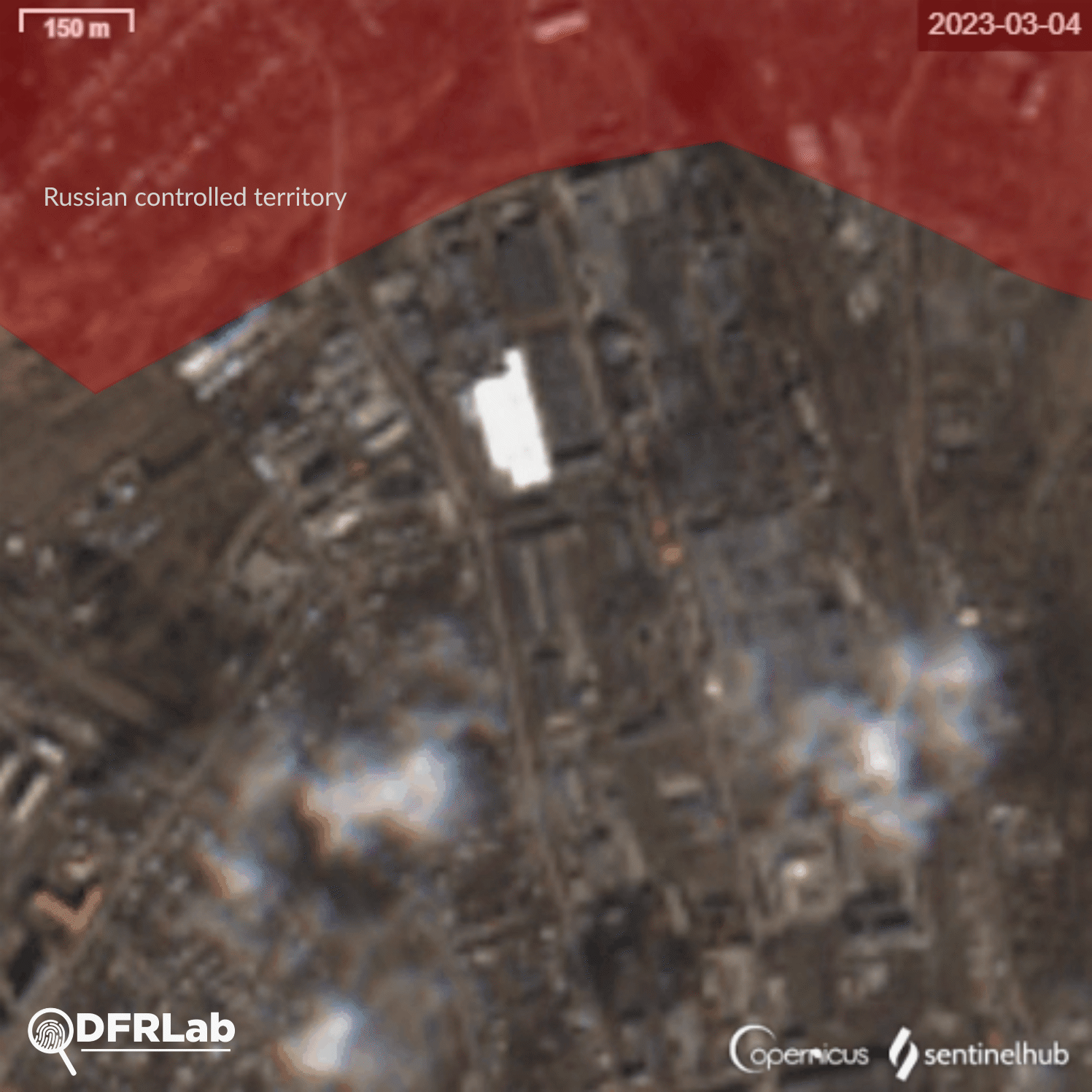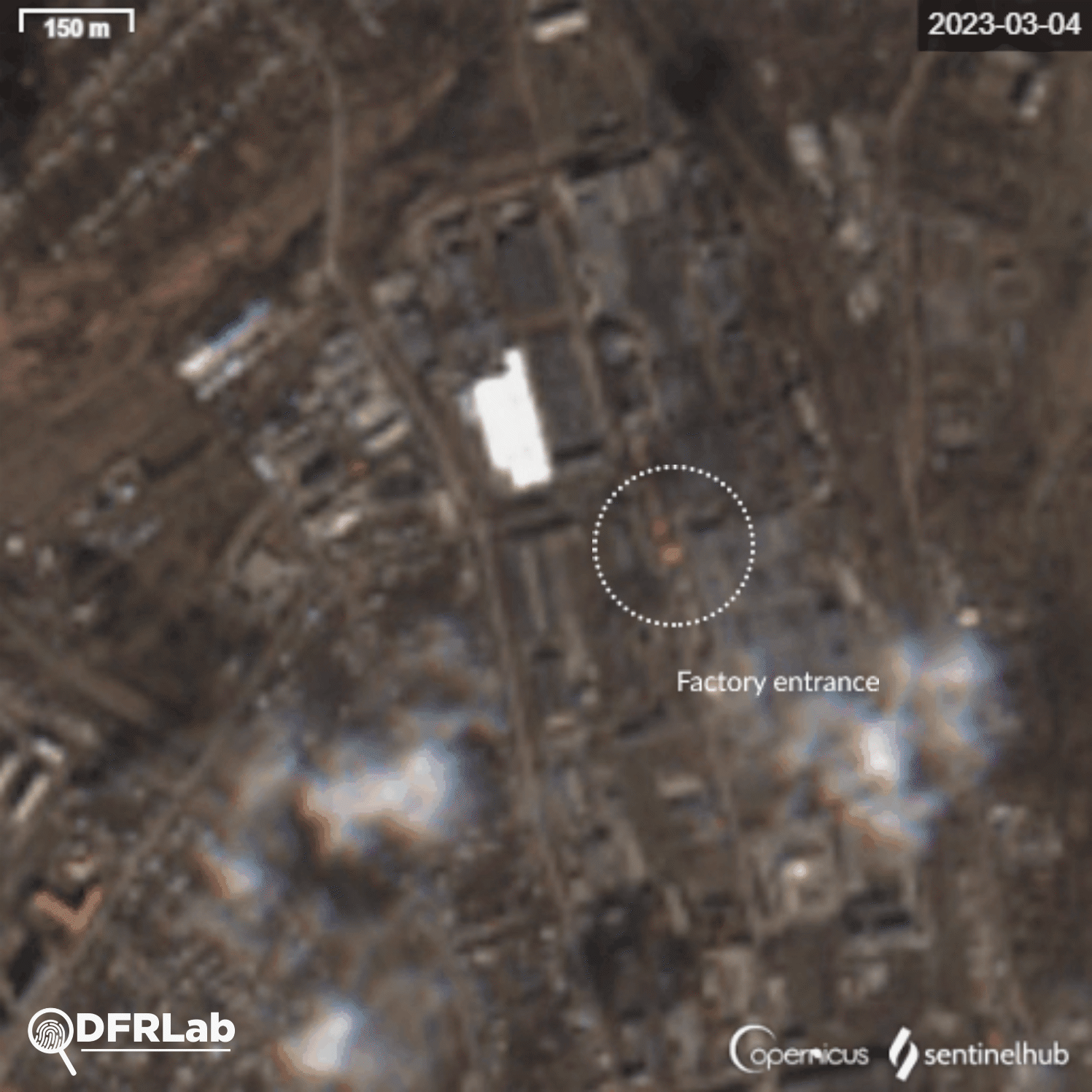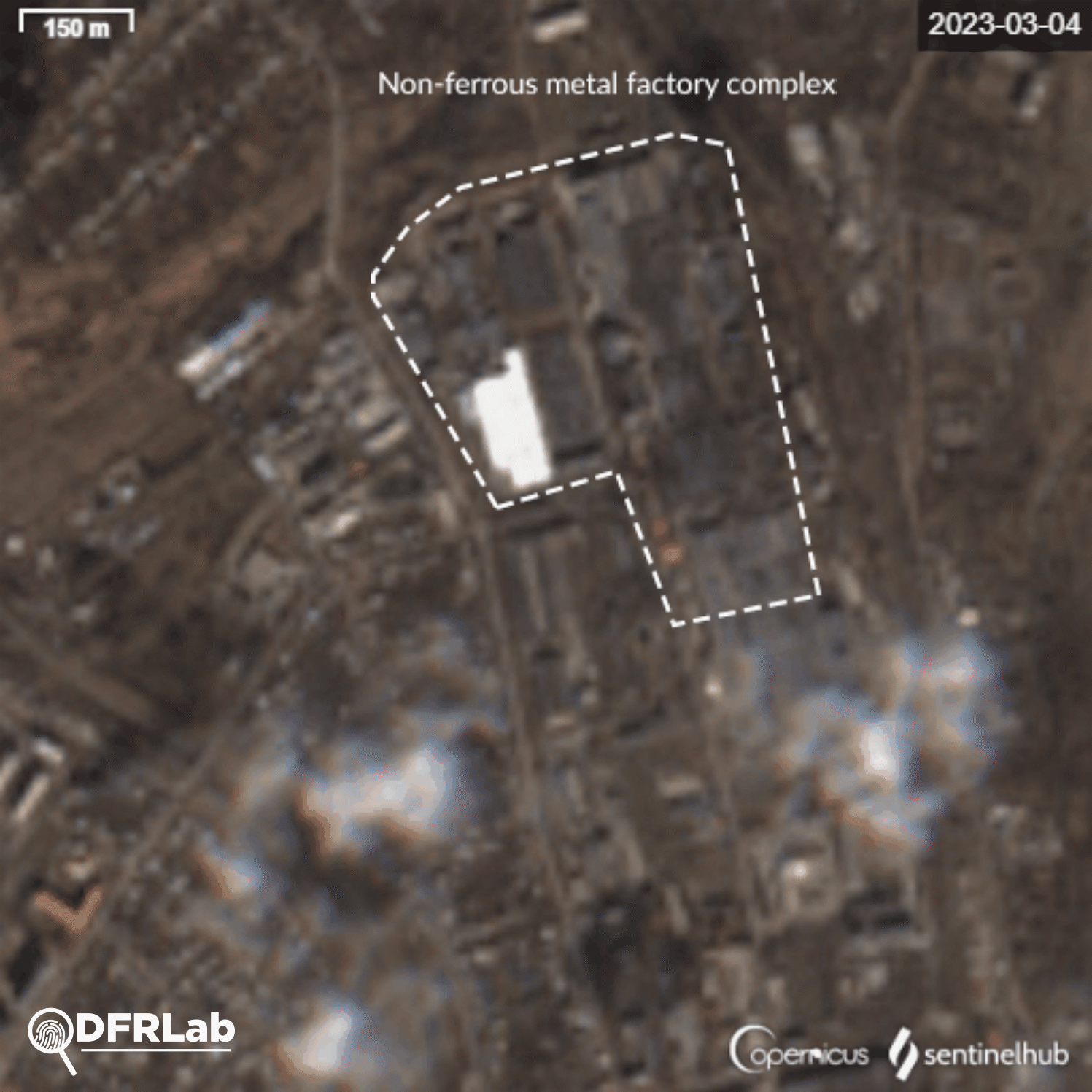
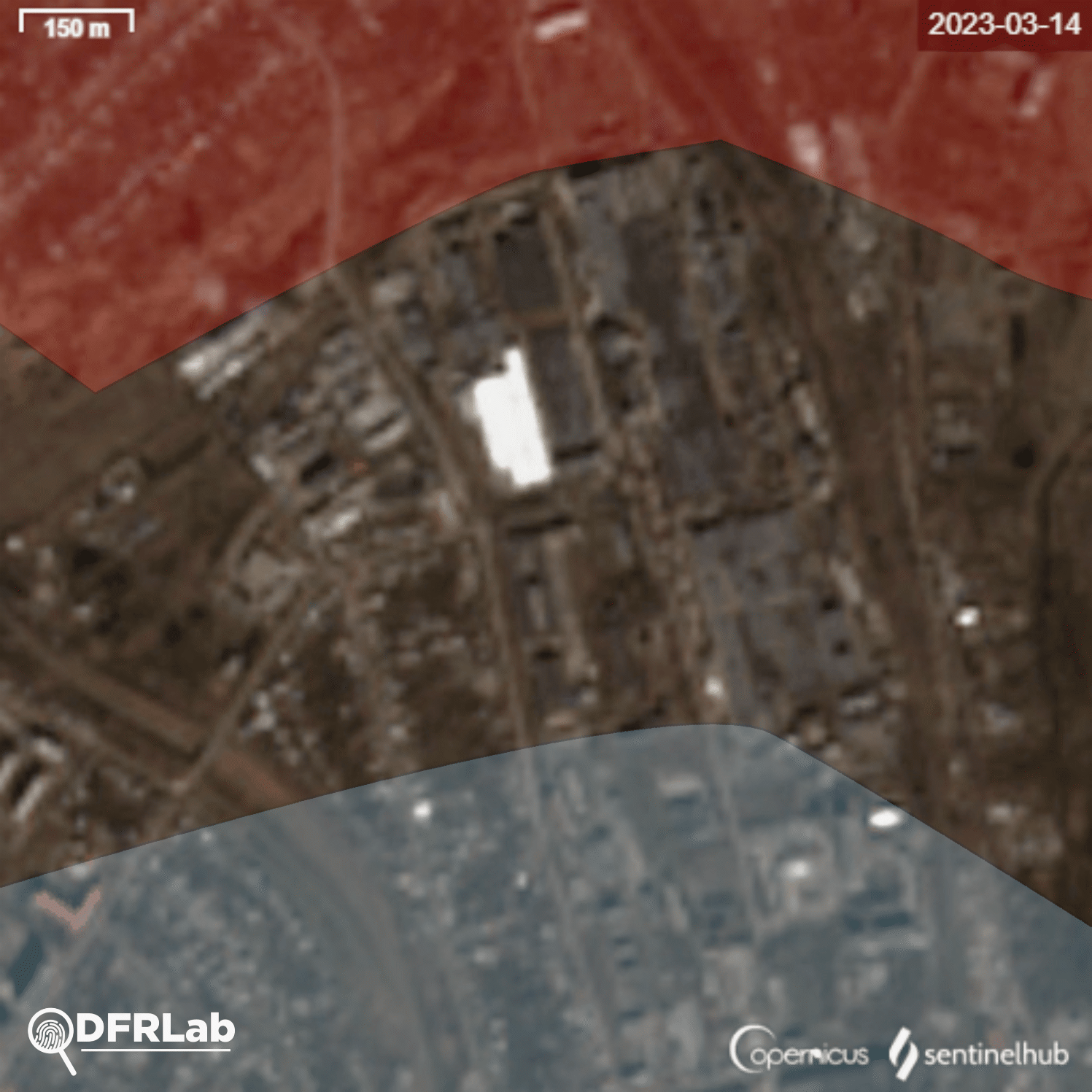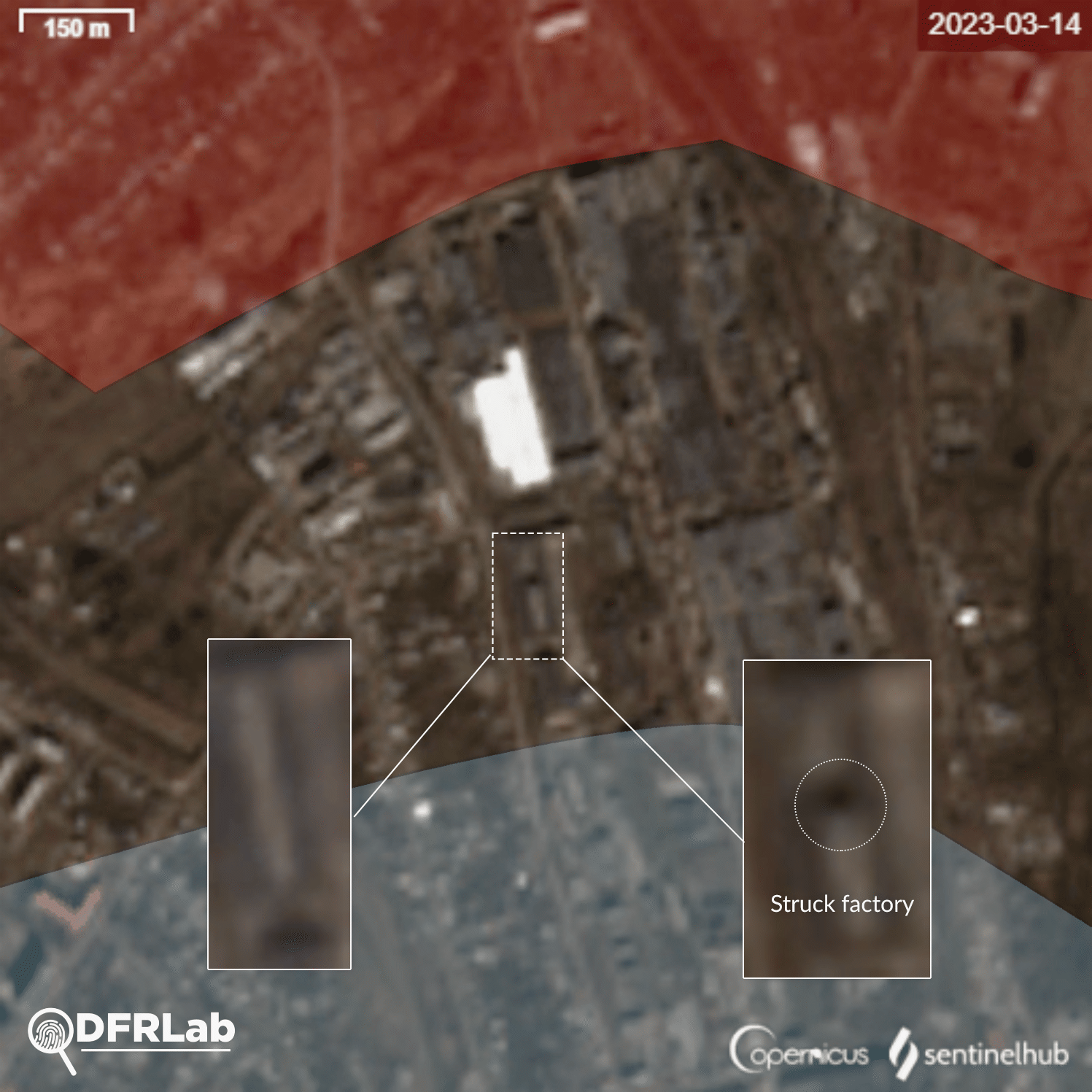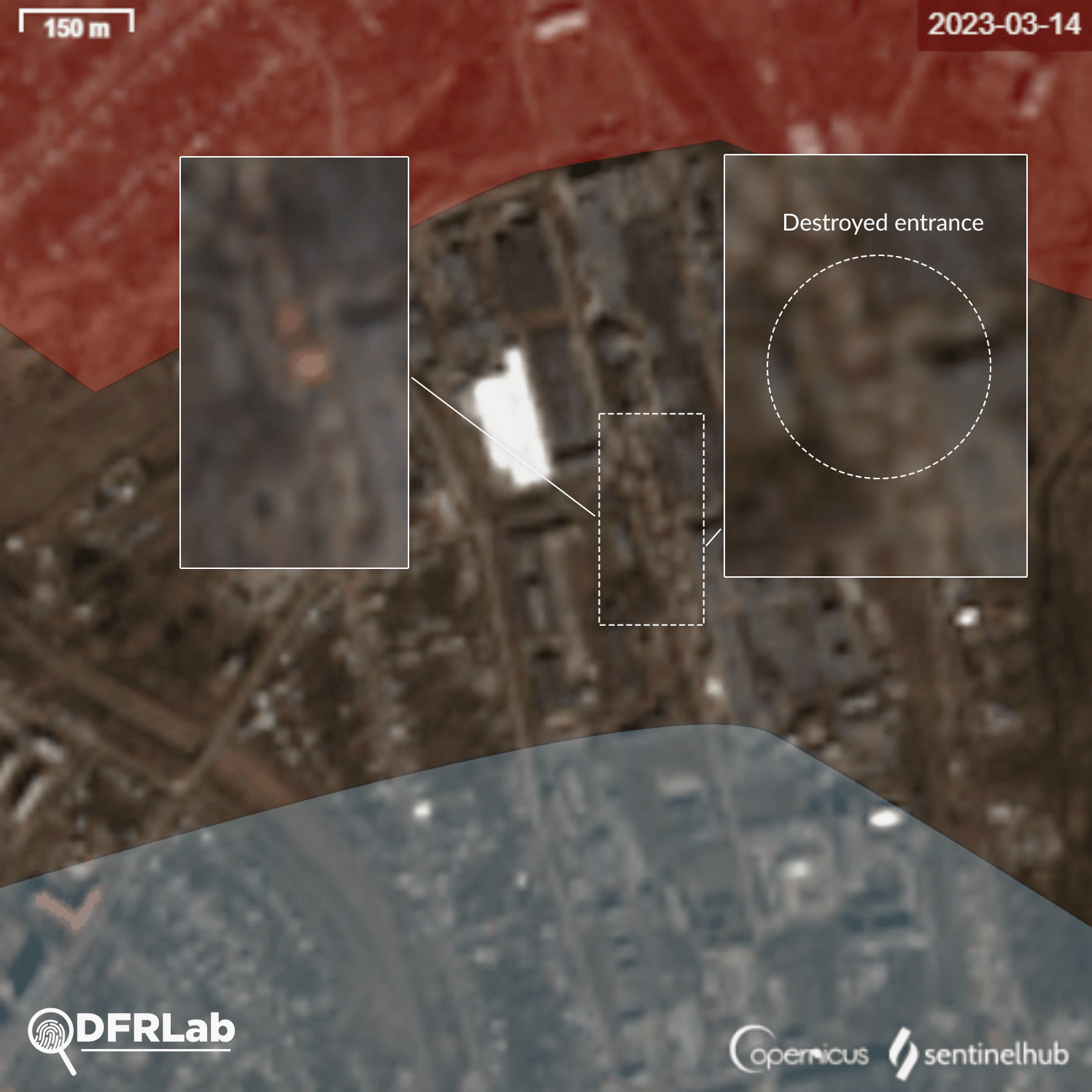
Analysis of the damage inflicted on buildings in the area reveals that potential missiles struck buildings belonging to two different industrial plants. The easternmost plant is the Bakhmut non-ferrous metals factory.
Satellite imagery showed the factory’s main building was destroyed, with a second building damaged. Traces of burns on the roof of the building can be seen from an explosion. This building belongs to the Makiivka metal construction plant.
—Valentin Châtelet, Research Associate, Security, Brussels, Belgium
Battle for Vuhledar highlights tensions between Wagner and Russian defense ministry
Eastern Ukraine continues to be a key arena for clashes as Russian forces attempt to advance in the directions of Vuhledar and Bakhmut. Ukrainian forces are using remote mining near Vuhledar, according to a March 16 report from UK defense intelligence. The remote anti-armor mine system (RAAMS) makes it possible to create an anti-tank minefield up to seventeen kilometers away from the firing unit. The United Kingdom reported that Ukraine was also firing the mines behind advancing Russian forces, leading to additional losses in the event of a retreat. The United Kingdom also reported that there is a “realistic possibility” that Russia’s push for Vuhledar is driven by the Russian defense ministry’s desire to produce better results than Wagner, who are driving Russia’s tactical progress towards Bakhmut.
The UK report supports the DFRLab’s analysis that the ongoing offensive operations in eastern Ukraine are provoking a competition between the different military units, particularly Wagner and the Russian defense ministry. In the direction of Bakhmut, Wagner’s forces continue to be the primary units fighting within the city. However, the combat has been difficult, and the urban environment makes progress challenging. In addition, Chechen forces in Bakhmut continue to fight alongside the Ukrainian army against Russian positions.
Russian forces are also having issues restoring tanks, according to a report published by Ukrainian outlet Defense Express. The 103rd armored repair plant in Russia has reportedly not been able to restore T-62 tanks under the terms originally contracted, which would have required the plant to restore twenty-two to twenty-three tanks per month. According to Defense Express, however, the real capacity of the plant is likely around seven tanks per month. On March 6, UK defense intelligence reported that Russia was deploying outdated T-62 tanks to the battlefield due to major losses in armored equipment.
Acts of sabotage against occupying Russian forces continue in the direction of Kherson. On March 11, the Telegram channel of the pro-Ukraine resistance movement Atesh reported that its members blew up a railway line in the Kherson region, between Radensk and Abrykosivka. This appears to be an attempt by Atesh partisans to impede logistics for the Russian troops deployed in the area.
Ukraine has also reported new arrests of alleged Russian infiltrators. On March 16, the Security Service of Ukraine reported the detention of two women accused of tracking the movement of Ukrainian equipment in the interest of Russian intelligence. The women also allegedly photographed the results of attacks on Ukrainian facilities. One of the women reportedly worked as a nurse in Ukraine’s territorial defense combat unit.
—Ruslan Trad, Resident Fellow for Security Research, Sofia, Bulgaria
Russian channels amplify Quran desecration video
Footage emerged online on March 15 showing the burning of the Islamic holy book, the Quran. Russian social media channels shared the one minute and six second video, accusing Ukrainian soldiers of being behind the desecration. The video sparked a wave of reactions on social media, particularly on Twitter, where a TikTok version of the video went viral. The TikTok video has since been removed.
The video is difficult to analyze and cannot be verified. It does not show the faces of the alleged Ukrainian soldiers. The people in the video are speaking broken Ukrainian and use a Russian military knife, said Oleg Nikolenko, a spokesperson for Ukraine’s foreign ministry.
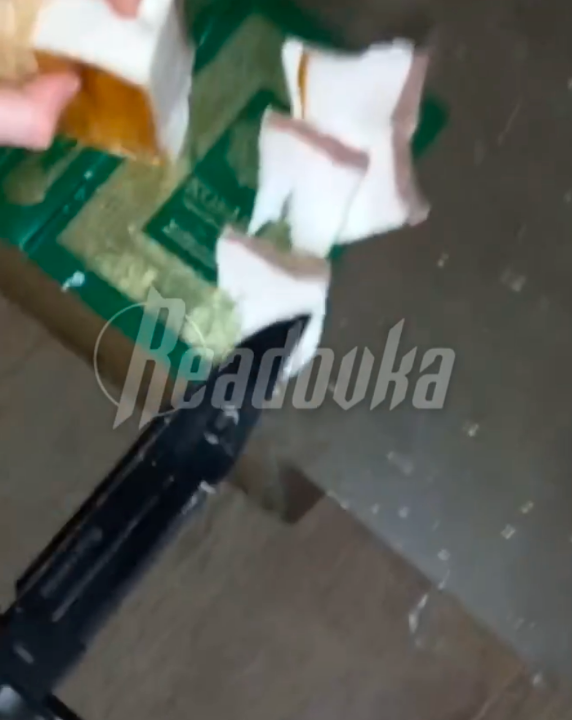

The video was denounced as a provocation by Said Imagilov, Mufti of the Spiritual Administration of Ukraine’s Muslims, as well as the Ukrainian military and Ukrainian officials.
Ukraine’s army has Muslim soldiers in its ranks, and Imagilov is an active participant on the frontlines defending Kyiv. The Ukrainian army is also supported by several Chechen units, the most well-known of which are the two volunteer battalions, the Dzhokhar Dudayev Battalion and the Sheikh Mansur Battalion. Chechens are among the most active defenders of Bakhmut, with their Adam special unit operating behind Russian army defense lines.
The provenance of the video remains unknown.
—Ruslan Trad, Resident Fellow for Security Research, Sofia, Bulgaria
European allies train Ukrainian forces on tank operation
Ukraine’s Western allies are continuing to help strengthen Kyiv’s defense against Russia by training Ukrainian troops on tank operation and trench warfare. Thierry Breton, European Commissioner for Internal Market, is visiting EU countries in a bid to shore up more ammunition for Ukraine. His first visit was to Bulgaria. This visit came as the Slovak news outlet Pravda published data on March 15 showing that, in the year since the February 2022 invasion of Ukraine, Slovakia has doubled its ammunition production and plans to double it again from current levels.
Meanwhile, Greece and the United States agreed to a deal that will see the US transfer 300 M2 Bradley fighting vehicles to the Greek army as part of a modernization program, according to Greek media reports on March 10. Greece is expected to send Ukraine BMP-1 vehicles and M113 armored carriers in exchange for the purchase of the Bradleys.
On March 13, Spain’s Ministry of Defense announced that ten Ukrainian crews completed training in Spain on operating Leopard 2 tanks. Along with fifty-five servicemen, fifteen Ukrainian technicians also received training. According to El Periódico, “These fifty-five soldiers – some professionals and other reservists – were already on the front line, and their four-week training lasted twelve hours a day.”
In addition, the German army announced it was training Ukrainian troops on the Leopard 2 tanks in Germany. “Training on the weapon systems is not just about how to use it, but also about tactics so that the Ukrainians can achieve the greatest possible effect against their opponents,” said Colonel Heiko Diehl.
Ukrainian servicemen in the United Kingdom also completed training in conducting trench combat in realistic conditions. The program was led by the 5th Battalion of the Royal Australian Regiment of the 1st Brigade of the Australian Defense Forces.
Earlier this week, Polish President Andrzej Duda announced that his country would send Ukraine thirty MiG 29 fighter jets. These are essential as Russia strives to achieve air dominance and has increased its aerial strikes throughout Ukraine. On March 14, a video emerged on Twitter showing Ukrainian soldiers taking part in trainings in the French military camp of Canjuers in the south of the country. The soldiers were reportedly training with the AMX-10RC armored personnel carriers. Minister of the Armed Forces of France Sebastien Lecornu confirmed during a defense commission hearing on March 15 that the carriers are already being delivered to Ukraine.
On March 15, the Israeli government approved licenses to export electronic warfare equipment to Ukraine that will help counter Iranian drones.
—Valentin Châtelet, Research Associate, Security, Brussels, Belgium
—Ruslan Trad, Resident Fellow for Security Research, Sofia, Bulgaria

